What S Key Generations In Forms
Here I share the Mercedes Benz EPC & EWA Net Keygen download link.This software without protection can move any device/hardware. EPC New Keygen Mhhauto. Copy your New License Key. For Testing your KEY with datacard or not. I give you the sample VIN number with the new cars. Jan 04, 2018 Benz New EPC & EWA Net Keygen Key Generator Free Download January 4, 2018 auto Auto Software Download & Installation 0 Here I share the Mercedes Benz EPC & EWA Net Keygen download link.This software without protection can move any device/hardware. Epc net license key generator. Hi All member Mhhauto I Wanna share My Key Generator for New EPC, Without Protection can move any device / hardware. No Password and no protection How To use?: 1. You must copy this code. Crack Keygen Mercedes Ewa Net Epc Wis Asra All Versions Torrent DOWNLOAD. Key Generators; Donate; Login Register: EPC SOFTWARE EPC SOFTWARE Categories Key. Porsche PIWIS II License Key Generator. 0: 64,882: 0 Vote(s) - 0 out of 5 in Average: Snap-on Catalogs Keygen v2.40 ALL Brands 0: 65,653. Mercedes EPC-NET Keygen With DATA Card.
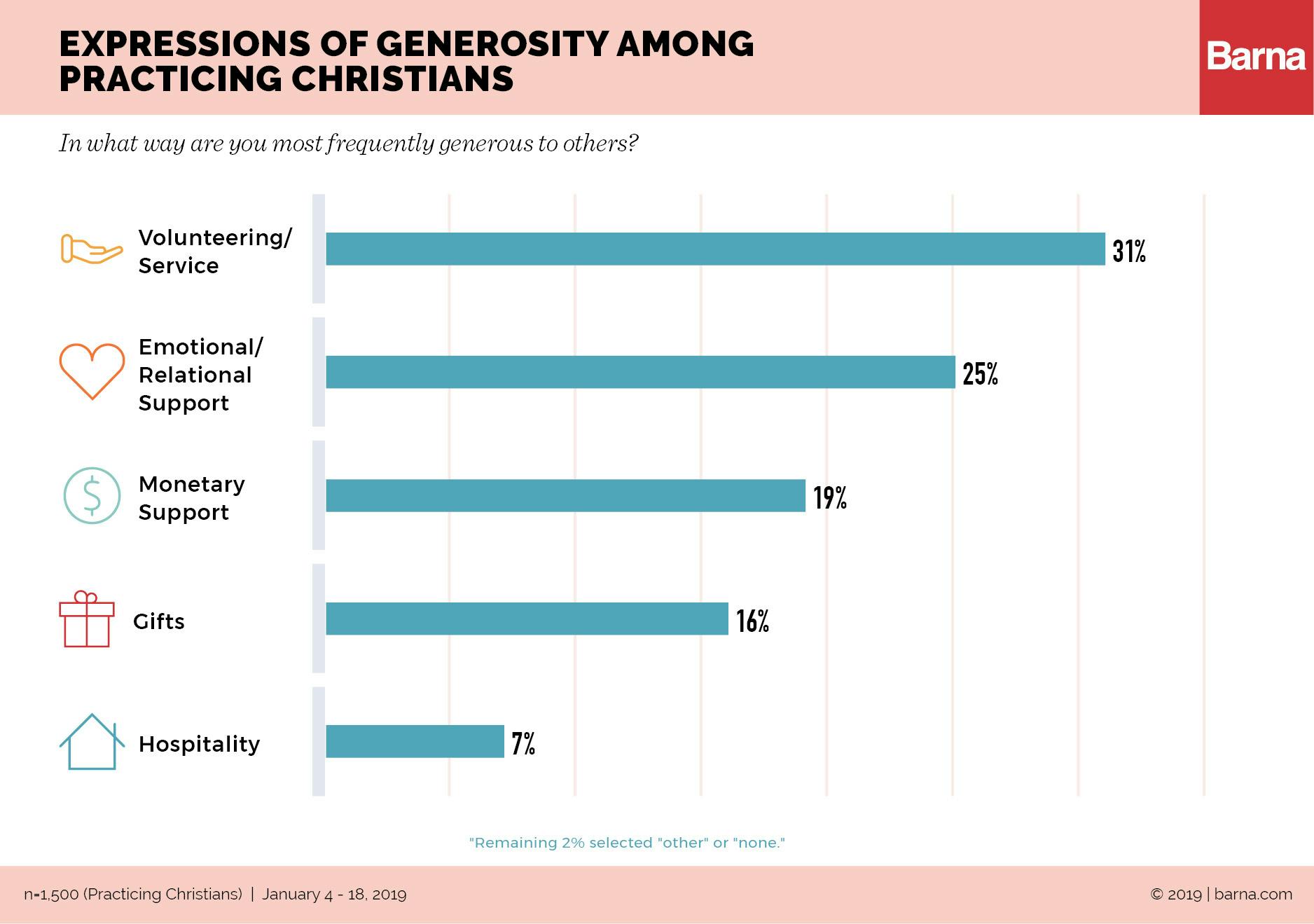
Want to stop spammers from filling out your forms? Google’s reCAPTCHA allows you to add human verification technology to your forms. WPForms makes it super easy to add reCAPTCHA to your forms. In this article, we will show you how to set up and enable the built-in reCAPTCHA integration in WPForms. What is reCAPTCHA? Generating reCAPTCHA Keys. To answer the question, key generation in forms is allowing the form to generate its own key based off a parameter and some other information likely stored on the server the website is hosted on.
But it’s more effective to have people on staff who can bring in the perspectives of different generations from the start. Provide Learning Opportunities Job training is great, but one of the best ways of helping your employees develop is by encouraging mentoring relationships, where one employee (usually more experienced) provides guidance. The name for the most recent generation is even more variable. Some prefer Generation Z, continuing the alphabetical trend begun with Generation X, while others prefer buzzier titles like Centennials or the iGeneration. What will come in the future is anyone's guess and with each new generation comes more disagreement. Feb 25, 2015 What does 4 Generations in The Market mean to you? Any given transaction will be key to winning this group's approval. Themselves with the generations who are most interested in their. In order to begin therapy, we will need to obtain some information from you, including a confidential case history, release of information form, our business policy/financial agreement, and our privacy policy. List below is checklist for your convenience. You may mail these to us or bring them to the first visit or fax them to 770.
Key generation is the process of generating keys in cryptography. A key is used to encrypt and decrypt whatever data is being encrypted/decrypted.
A device or program used to generate keys is called a key generator or keygen.
Generation in cryptography[edit]
Modern cryptographic systems include symmetric-key algorithms (such as DES and AES) and public-key algorithms (such as RSA). Symmetric-key algorithms use a single shared key; keeping data secret requires keeping this key secret. Public-key algorithms use a public key and a private key. The public key is made available to anyone (often by means of a digital certificate). A sender encrypts data with the receiver's public key; only the holder of the private key can decrypt this data.
Since public-key algorithms tend to be much slower than symmetric-key algorithms, modern systems such as TLS and SSH use a combination of the two: one party receives the other's public key, and encrypts a small piece of data (either a symmetric key or some data used to generate it). The remainder of the conversation uses a (typically faster) symmetric-key algorithm for encryption.
Computer cryptography uses integers for keys. In some cases keys are randomly generated using a random number generator (RNG) or pseudorandom number generator (PRNG). A PRNG is a computeralgorithm that produces data that appears random under analysis. PRNGs that use system entropy to seed data generally produce better results, since this makes the initial conditions of the PRNG much more difficult for an attacker to guess. Another way to generate randomness is to utilize information outside the system. veracrypt (a disk encryption software) utilizes user mouse movements to generate unique seeds, in which users are encouraged to move their mouse sporadically. In other situations, the key is derived deterministically using a passphrase and a key derivation function.
Many modern protocols are designed to have forward secrecy, which requires generating a fresh new shared key for each session.
Classic cryptosystems invariably generate two identical keys at one end of the communication link and somehow transport one of the keys to the other end of the link.However, it simplifies key management to use Diffie–Hellman key exchange instead.
The simplest method to read encrypted data without actually decrypting it is a brute-force attack—simply attempting every number, up to the maximum length of the key. Therefore, it is important to use a sufficiently long key length; longer keys take exponentially longer to attack, rendering a brute-force attack impractical. Currently, key lengths of 128 bits (for symmetric key algorithms) and 2048 bits (for public-key algorithms) are common.
Generation in physical layer[edit]
Wireless channels[edit]
A wireless channel is characterized by its two end users. By transmitting pilot signals, these two users can estimate the channel between them and use the channel information to generate a key which is secret only to them.[1] The common secret key for a group of users can be generated based on the channel of each pair of users.[2]
Optical fiber[edit]
A key can also be generated by exploiting the phase fluctuation in a fiber link.[clarification needed]
See also[edit]
- Distributed key generation: For some protocols, no party should be in the sole possession of the secret key. Rather, during distributed key generation, every party obtains a share of the key. A threshold of the participating parties need to cooperate to achieve a cryptographic task, such as decrypting a message.
References[edit]
- ^Chan Dai Truyen Thai; Jemin Lee; Tony Q. S. Quek (Feb 2016). 'Physical-Layer Secret Key Generation with Colluding Untrusted Relays'. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications. 15 (2): 1517–1530. doi:10.1109/TWC.2015.2491935.
- ^Chan Dai Truyen Thai; Jemin Lee; Tony Q. S. Quek (Dec 2015). 'Secret Group Key Generation in Physical Layer for Mesh Topology'. 2015 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM). San Diego. pp. 1–6. doi:10.1109/GLOCOM.2015.7417477.
Updated on March 30, 2020
Spend enough time in an IT environment and you will likely come across the term SSH keys. If you’ve already come across this IT term, then you might find yourself wondering, what are SSH keys? SSH (Secure Shell) keys are an access credential that is used in the SSH protocol.
Read the rest of this post to learn more about what are SSH keys or consider watching webinar below to find out more about the SSH protocol and the basics of SSH authentication.
Before this post delves into an explanation on what are SSH keys, let’s take a quick look at the SSH protocol.
The SSH Protocol
The first version of the SSH protocol was developed in the summer of 1995 by Tatu Ylonen. Tatu was a researcher at the University of Helsinki when a sniffing attack was discovered on the university network. A sniffing attack intercepts and logs the traffic that takes place on a network, and can provide attackers with usernames and passwords which can then be used to gain access to critical IT assets. Thousands of credentials were impacted, including those belonging to community partnerships. This sniffing attack motivated Tatu to figure out how to make networks more secure, and this ultimately led to the creation of the SSH protocol (SSH.com).
Today, the SSH protocol is widely used to login remotely from one system into another, and its strong encryption makes it ideal to carry out tasks such as issuing remote commands and remotely managing network infrastructure and other vital system components. To use the SSH protocol, a couple pieces of software need to be installed. The remote systems need to have a piece of software called an SSH daemon, and the system used to issue commands and manage the remote servers needs to have a piece of software called the SSH client. These pieces of software are necessary to create a proper communication channel using the SSH protocol (DigitalOcean).
Essentially, SSH keys are an authentication method used to gain access to this encrypted connection between systems.
What are SSH keys?
SSH keys come in many sizes, but a popular choice is RSA 2048-bit encryption, which is comparative to a 617 digit long password. On Windows systems, it is possible to generate your own SSH key pair by downloading and using an SSH client like PuTTY. On Mac® and Linux® systems, it is possible to generate an SSH key pair using a terminal window. Watch the video below to find out how to generate your own RSA key pair on Mac and Linux.
SSH keys always come in pairs, and each pair is made up of a private key and a public key. Who or what possesses these keys determines the type of SSH key pair. If the private key and the public key remain with the user, this set of SSH keys is referred to as user keys. If the private and public key are on a remote system, then this key pair is referred to as host keys. Another type of SSH key is a session key. When a large amount of data is being transmitted, session keys are used to encrypt this information.
Now let’s take a closer look at how a private key and public key work. To keep things simple, we will focus on how user keys work.
How User Keys Work
In a user key set, the private key remains on the system being used to access the remote system and is used to decrypt information that is exchanged in the SSH protocol. Private keys should never be shared with anyone. A public key is used to encrypt information, can be shared, and is used by the user and the remote server. On the server end, the public key is saved in a file that contains a list of authorized public keys. On the user’s side, the public SSH key is stored in an SSH key management software or in a file on their computer.
Nov 13, 2018 Click on Generate key, then wait a few moments for the program to produce your key. Importing an old key pair. If you already have an existing key pair which you would like to use, go to Thunderbird’s menu, then put your cursor over the Enigmail option which pops up. Click on Key Management, which opens up in the new menu. Free pgp key software. PGP Private Key Save your PGP private key in a file on your computer and keep it as confidential as possible. Use copy & paste to a text editor such as Notepad to save your PGP key.
Using SSH Keys
First Steps
Before you can start using SSH keys, first you need to generate your own SSH key pair on the system you would like to use to access a remote system. This article and the video mentioned above are great resources that can guide you through on how to generate an SSH key pair. Once the key pair is generated, the next step is to put the public SSH key on the remote server. Depending on your setup, this can be done by entering a couple commands in the terminal window, using JumpCloud, or by manually placing the public SSH key on the remote server (DigitalOcean).
Behind the Scenes of SSH Key Authentication
After completing the steps mentioned above, use your terminal to enter in your ssh username and the IP address of the remote system in this format: ssh username@my_ip_address. This will initiate a connection to the remote system using the SSH protocol. The protocol and specified username will then tell the remote server which public key to use to authenticate you. Then the remote server will use that public key to encrypt a random challenge message that is sent back to the client. This challenge message is decrypted using the private key on your system. Once the message is decrypted, it is combined with a previously arranged session ID and then sent back to the server. If the message matches with what the server sent out, the client is authenticated, and you will gain access to the remote server. This process proves to the server that you have the corresponding private key to the public key it has on file.
However, the security that this authentication process provides can be undermined when SSH keys are not properly managed.
Managing SSH Keys
It is imperative that proper SSH key management is in place because they often grant access to mission-critical digital assets. Also, companies tend to have a lot of SSH keys. In fact, Fortune 500 companies will often have several millions of these. Despite the difficulty in trying to manually manage millions of SSH keys, having an SSH key management system in place is continuously overlooked. SSH.com did some digging and discovered a company that had 3 million SSH keys “that granted access to live production servers. Of those, 90% were no longer used. Root access was granted by 10% of the keys, ” (SSH.com). An effective SSH key management system in place would have gone a long way in reducing this concerning security risk.
IT has a couple options to gain control over SSH keys in their environment. One of these includes using an SSH key management tool. However, this means having to manage one more platform in addition to managing an SSO provider, a directory service, and maybe a system management solution. A new solution has emerged that is providing IT with a second option: Directory-as-a-Service®.
Cloud IAM offers SSH Key Management
This cloud-based identity and access management (IAM) solution provides IT with one central place to manage SSH keys. Furthermore, IT can also centralize user authentication to Mac, Linux, and Windows systems, cloud servers, wired and WiFi networks, web-based and on-prem applications, and virtual and on-prem storage. With one central place to manage a user’s authentication to all of their resources, it becomes a simple matter of a few clicks to deprovision users from all of their resources, including SSH key access to remote systems.
Free Key Generation Software
Learn More about SSH Key Management with JumpCloud
What Is Key Generation In Forms 2017
For more information, consider reading this support article on how JumpCloud assists with SSH key management, or exploring this guide for a modern approach to managing user accounts on your cloud servers.
You are also more than welcome to reach out to us if you would like more information on how DaaS can simplify your SSH key management. If you’re ready to start testing our modern IAM platform, sign up for a free account. You’ll be able to explore all of our features, and your first ten users are free forever.